Ensemble Space Inversion
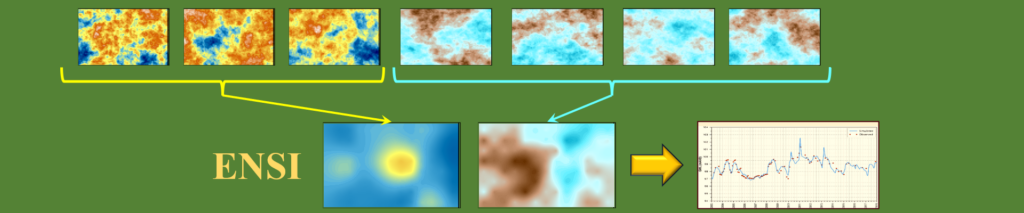
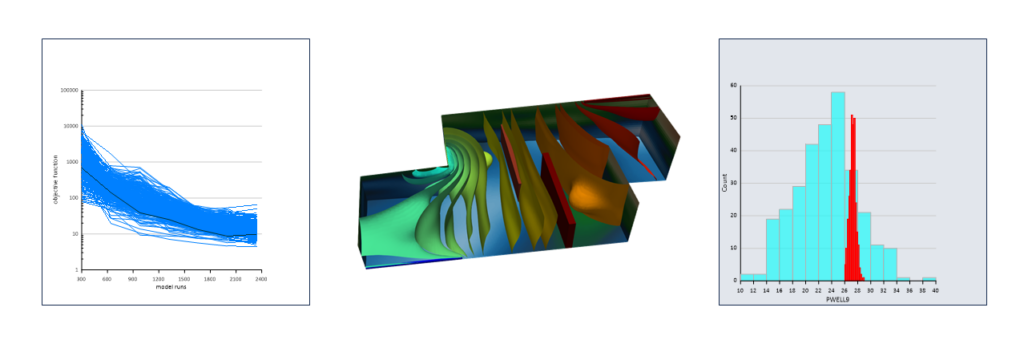
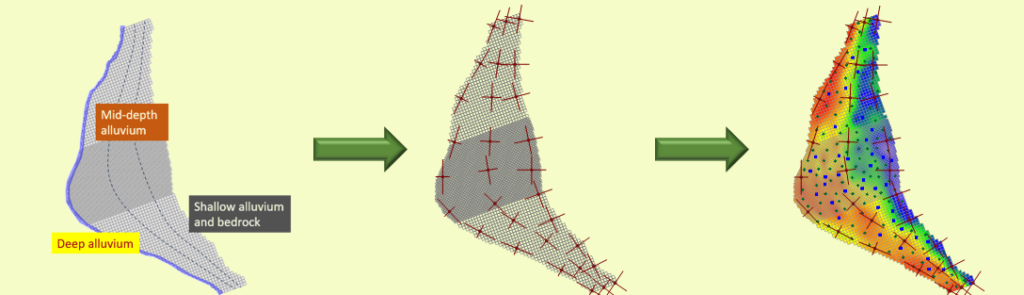
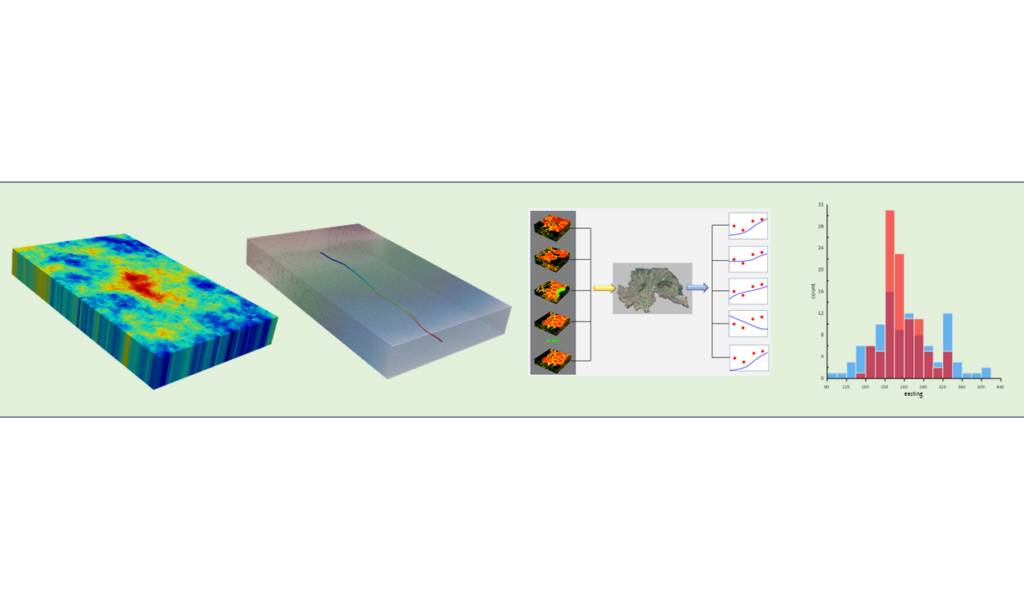
Ensemble space inversion (ENSI) is implemented through the PEST_HP suite (version 18). Using ENSI you can calibrate a complex model quickly. The calibration subspace is comprised of random parameter realisations as well as individual parameters. Realisations can be different for different parameter types. Regularisation seeks a minimum error variance solution within the confines of the working […]
Ensemble Space Inversion Read More »